Abdominal ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of abdominal organs holds a primary place among all diagnostic methods due to its high informativeness, non-invasiveness, and the ability to repeat the examination multiple times in dynamics without harming the patient's health. The high degree of visualization capability of the equipment enhances the ability to detect pathologies and provides a more accurate picture of the microstructure of tissues, which improves the effectiveness of diagnosis and treatment in the early stages of disease development.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity organs is one of the most well-known diagnostic methods. This method uses high-frequency sound waves to get images of internal organs, which allows doctors to assess the condition of the internal organs and identify various pathologies. Abdominal ultrasound is a safe, painless and non-invasive research method that has no contraindications and can be performed at any age.
Indications
- Abdominal pain of unknown origin
- Suspecting diseases of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen or kidneys.
- Diagnosis of tumors and cysts
- Inflammatory processes (hepatitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis)
- Abdominal trauma
- Presence of jaundice
- Evaluating the conditions of the organs after the operation.
- Monitoring chronic diseases
Ultrasound examination is also often performed during different therapeutic procedures.
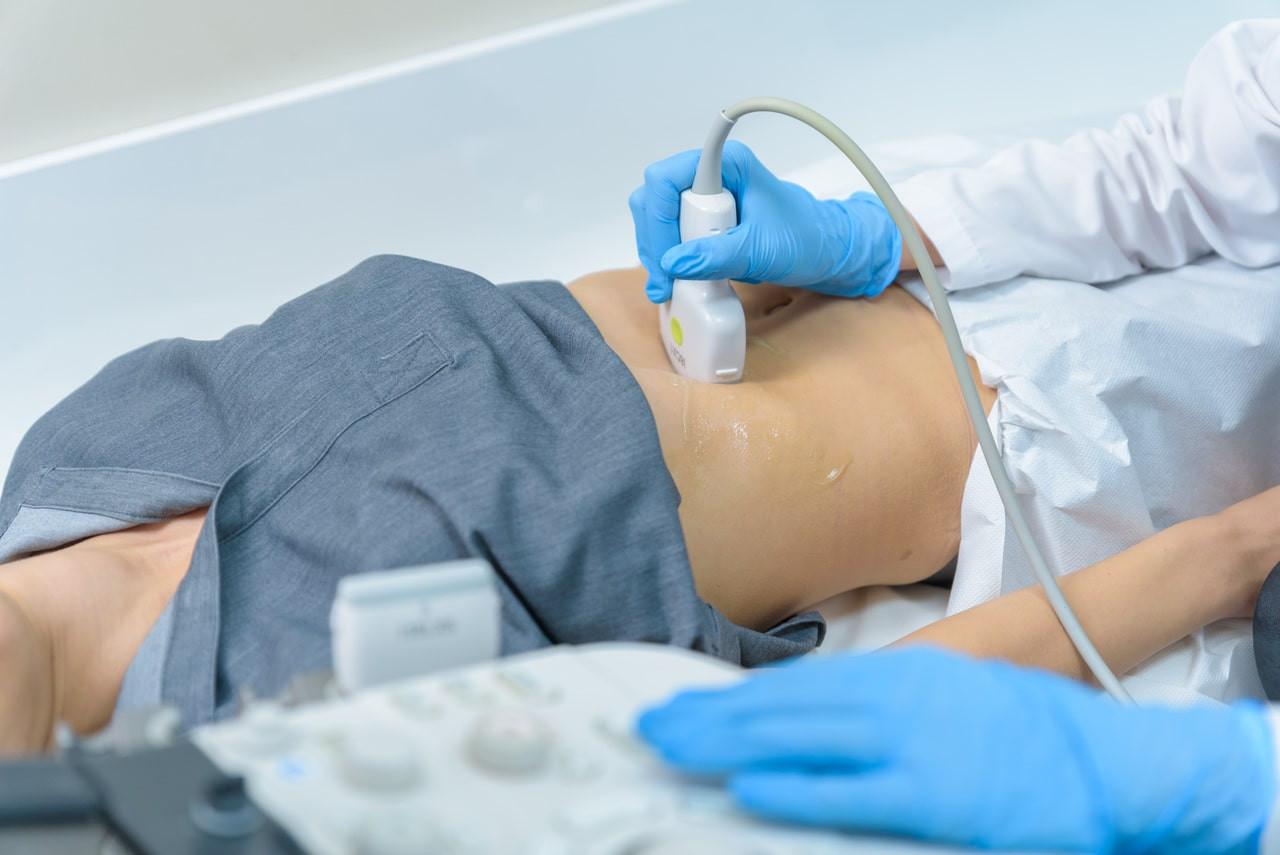
What organs are examined?
When performing an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, the following organs are examined:
- Liver: assessment of the size, structure, presence of any neoplasms (tumors, cysts), as well as signs of inflammation, or steatotic liver disease.
- Detection of the stones, inflammatory processes (cholecystitis), polyps and other pathologies in the gallbladder and biliary tract.
- Pancreas: assessment of the size and structure, determination of any inflammatory processes (pancreatitis), cysts or tumors:
- Spleen: assessment of the size and structure, detection of the presence of an enlargement (splenomegaly), cysts or tumors:
- Kidneys and adrenal glands: assessment of the size and structure, detection of stones, cysts, tumors and signs of inflammation present.
- Assessment of the condition of the bladder walls, detection of stones, tumors and other abnormalities.
- Large vessels in the abdominal cavity: asessment of the abdominal aorta and other large vessels of the cavity, detection of any aneurysms or other vascular pathologies present.
To obtain more accurate results from an abdominal cavity ultrasound, it is required to perform some preparatory actions.
1. Diet. 2-3 days before getting an examination, it is recommended to exclude products that cause intestinal gas formation (black bread, dairy products, legumes, cabbage, sweets, carbonated drinks).
2. Medication intake: in some cases, the doctor may recommend taking medications that reduce intestinal gas formation (Espumizan for example).
3. Fullness of the bladder. 1-2 hours before the ultrasound, it is recommended to drink 1-1.5 liters of water to fill the bladder, which will improve the vision of the organs.
Where can you undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal organs in Yerevan?
To undergo ultrasound of the abdominal organs in Yerevan, you can contact Nairi medical center, which is equipped with modern technologies and has a wide range of medical services provided. The Nairi MC is located in Yerevan, Paronyan street 21 address. You can call 8900 to get registered or to be provided with more detailed information.
List of services
- ▸ Plasmapheresis
- ▸ “Longevity Nairi”
- ▸ Laboratory Diagnosis
- ▸ Computed Tomography
- ▸ Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- ▸ Mammography
- ▸ X-Ray Diagnostics
- ▸ Ultrasound Diagnostics
- ▸ Endoscopic Diagnosis
- ▸ Functional diagnostics
- ▸ Electroneuromyography (ENMG)
- ▸ Electroencephalography (EEG)
- ▸ Vascular Ultrasound or Duplex Scan
- ▸ Kidney CT Scan
- ▸ Ultrasound (US) of the Lower Limbs
- ▸ Lymph Node Ultrasound (USG)
- ▸ CT Scan of the Heart
- ▸ CT Scan of the Liver
- ▸ Breast Ultrasound
- ▸ Pelvic Ultrasound
- ▸ Thyroid ultrasound
- ▸ Kidney Ultrasound
- ▸ Liver Ultrasound
- ▸ Ultrasound of the ovaries
- ▸ Ultrasound of the heart
- ▸ Abdominal ultrasound
- ▸ Ultrasound during pregnancy
- ▸ CT of paranasal sinuses
- ▸ Computed tomography of the chest
- ▸ Head/brain computed tomography
- ▸ Abdominal computed tomography
- ▸ Spinal MRI
- ▸ Joint MRI
- ▸ Brain MRI






